- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- A kick-starter guide to automating your order management process
A kick-starter guide to automating your order management process
- Last Updated : April 24, 2025
- 103 Views
- 7 Min Read
You may be running a business or working a regular job, but behind the scenes, we’re all customers too. Picture this: You place an order online, but there’s a delay in confirmation. You wait for updates that never arrive, and when the package finally shows up, it's either late, incomplete, or not what you expected. Doesn’t feel great, does it?
Now flip that. When planning to create and automate your business's order management system, think from your customers' point of view. What would make their experience smoother, faster, and more reliable?
This article is your go-to guide to help you plan, map, and automate your order management system so it actually delivers—every step of the way.
4 key steps to consider before automation
Building an efficient automation system for your business processes doesn't happen overnight, which is why we've laid out four important steps you need to reach your goal:
1. Recognizing the bottlenecks in your order management process
Before you start to automate the order management process at your business, you need to understand any current process bottlenecks. What are the areas in your order processing that are taking too much time? Maybe it’s something like data entry, order validation, or communication with customers.
To identify these bottlenecks, you can use a fish-bone or Ishikawa diagram. This method helps you map out the problem, identify its root causes, and find solutions. By visualizing your process, you can pinpoint areas that need attention, making it easier to apply automation where it’s most needed.
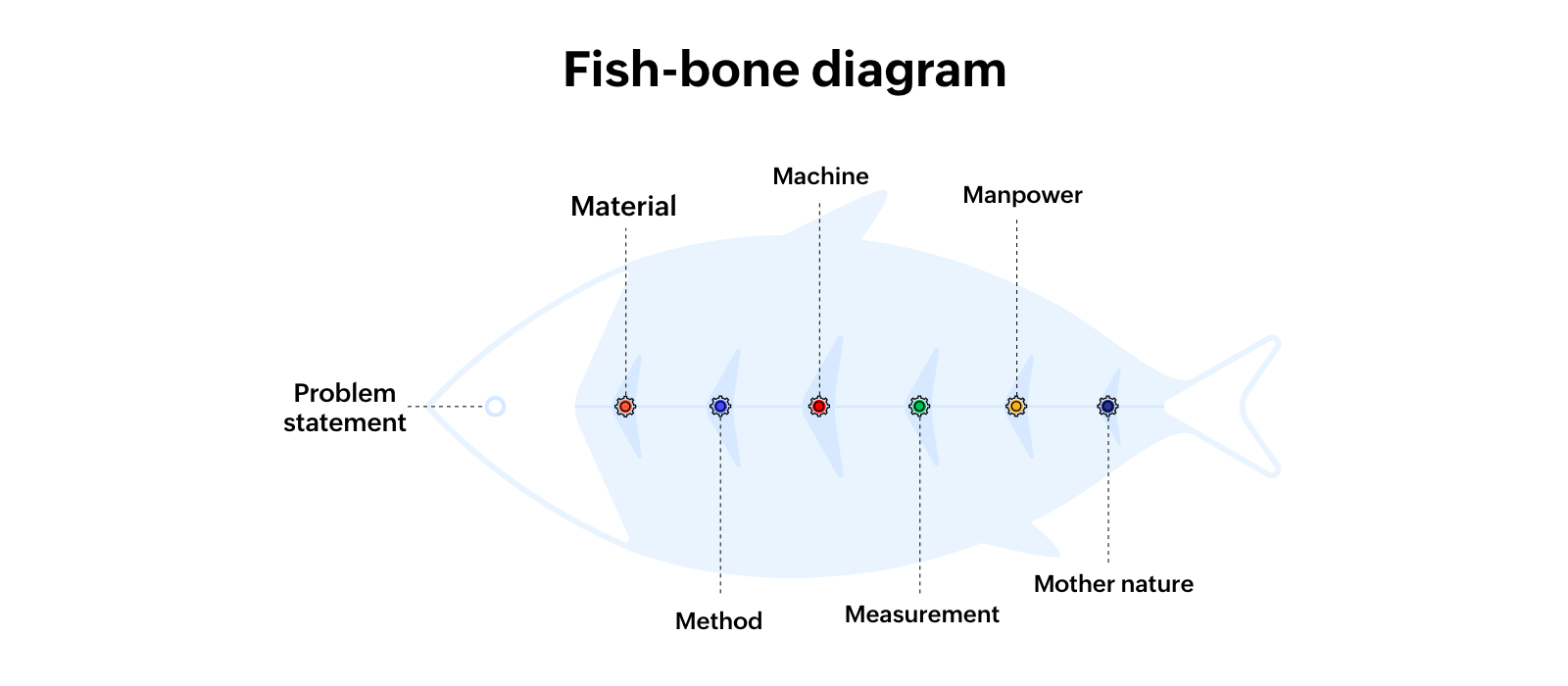
How to use a fish-bone diagram
a. Define the problem: Write the main challenge at the "head" of the diagram.
b. Identify major categories: Draw lines branching from the "spine" to represent contributing factors, such as:
Material: Resources and tools involved
Quality of the materials
Inventory levels
Issues with suppliers
Method/process: Repetitive procedures and workflows
Outdated practices
Inefficient processes
Lack of standard operating procedures (SOPs)
Machine: Equipment or software used
Faulty machinery
Outdated software
Lack of automation tools
Measurement: Performance and quality tracking
Inaccurate data
Lack of key performance indicators (KPIs)
Improper measurement tools
Manpower: The workforce managing the operations
Skills of the workforce
Training deficiencies
Communication issues
Staffing shortages
Human errors
Mother nature: External factors affecting the system
Weather conditions
Regulatory changes
Economic conditions
External environmental influences
c. Analyze: Review the diagram to determine root causes and focus automation efforts on key pain points.
2. Integrating with your sales channels
If you're selling through multiple channels, it's important to ensure that your order management system integrates with them seamlessly. Having all your data flow into one central system helps track orders in real time, eliminating errors caused by manual entry. These errors often happen when team members input the same order details into multiple systems. This increases the chances of typos, missing data, or mismatched inventory counts. Whether you manage orders from an online store, brick-and-mortar shop, or third-party marketplace, integration is essential for efficiency.
3. Mapping out your full order journey
Understanding your customer’s journey with you is critical when setting up any process automation. For example, if you're an ecommerce platform, the journey could be:
Order confirmation → Payment processing → Order fulfillment → Shipping → Delivery → Post-delivery services
As you map out the journey, consider the actions, mindsets, and emotions of your customers at each stage to improve customer experience (CX):
Actions: Steps that customers take during each phase of their journey.
Mindsets: Customer's thoughts and motivations as they move through the process.
Emotions: What could the customer be feeling (happiness/frustration/sad) during the various steps in the order journey.
4. Deciding what actions will trigger automation
Automation only works smoothly when you set the right triggers. A trigger is the event that starts a workflow based on a specific event, such as form submission or data input. To plan where to add triggers, focus on key events in your order journey after completing the previous checkpoints. These triggers should be set based on actionable events, such as:
Payment confirmation → Invoice generation
Order fulfillment → Inventory updating
Order shipment → Tracking details sent to the customer
Delivery confirmation → Customer feedback request
Ensure that each action in the order management process (from order placement to delivery) is tied to a clear automated response. This will keep the process efficient and streamlined.
Where to set up automation in your order management process flow
Now that you’ve covered the key checkpoints, let’s take a look at how to structure your order management process. This roadmap outlines the places to set up the automation in your order management system from start to finish. An effective order management workflow includes key automation triggers that ensure smooth processing and minimal manual intervention.
1. Order capture and data entry
Integrate multiple sales channels (website, marketplace, POS) into a centralized order management system (OMS).
Enable real-time order sync to avoid manual data entry and ensure all orders are captured correctly.
Set up auto-tagging for order priority, such as express shipping, bulk orders, and high-value orders.
2. Order validation and verification
Enable fraud detection workflows that flag suspicious transactions based on predefined criteria like high-value orders and mismatched billing/shipping addresses.
Automate duplicate order detection and merge duplicate customer profiles.
Use validation rules to check missing or incorrect customer details, like incomplete addresses.
Auto-check real-time inventory levels before confirming an order to prevent overselling.
3. Payment confirmation and invoicing
Integrate payment gateways like Stripe, PayPal, and Square for instant payment verification.
Set up automated workflows to trigger order confirmation once payment is received.
Auto-generate invoices and send them via email or customer portal.
Implement failed payment alerts with automated retry attempts and alternative payment prompts.
4. Order fulfillment and inventory allocation
Configure order routing automation to assign fulfillment based on warehouse location and stock availability.
Trigger warehouse picking, packing, and fulfillment workflows upon order confirmation.
Enable automated alerts for low inventory and back-order notifications.
5. Shipping and delivery
Auto-generate shipping labels and assign carriers based on delivery speed, cost, or region.
Automate tracking number assignment and send updates to customers.
Set up smart shipping rules to determine the fastest or most cost-effective carrier automatically.
Auto-update estimated delivery time based on real-time carrier data.
6. Customer communication and notifications
Set up automated email/SMS notifications for order confirmation, shipping updates, and estimated delivery.
Implement chatbots or AI-driven customer service to handle order status inquiries.
Automate delivery delay notifications and proactive resolution workflows.
Set up personalized post-purchase follow-ups and feedback requests.
7. Returns and refund management
Launch an online return request portal with automated eligibility checks.
Auto-generate return shipping labels for approved return requests.
Automate refund processing and update inventory upon return completion.
Implement exchange workflows with suggested alternative products.
8. Post-order analytics and reporting
Auto-generate reports on order trends, fulfillment performance, and return rates.
Set up real-time dashboards for monitoring sales, stock levels, and customer behavior.
Use AI-driven analytics to predict demand and optimize inventory.
Automate scheduled reporting to send daily/weekly/monthly insights to key stakeholders.
Examples to consider for order management automation
Here’s how automation can streamline different order management workflows with clear processes and a few practical examples of how they can be set up:
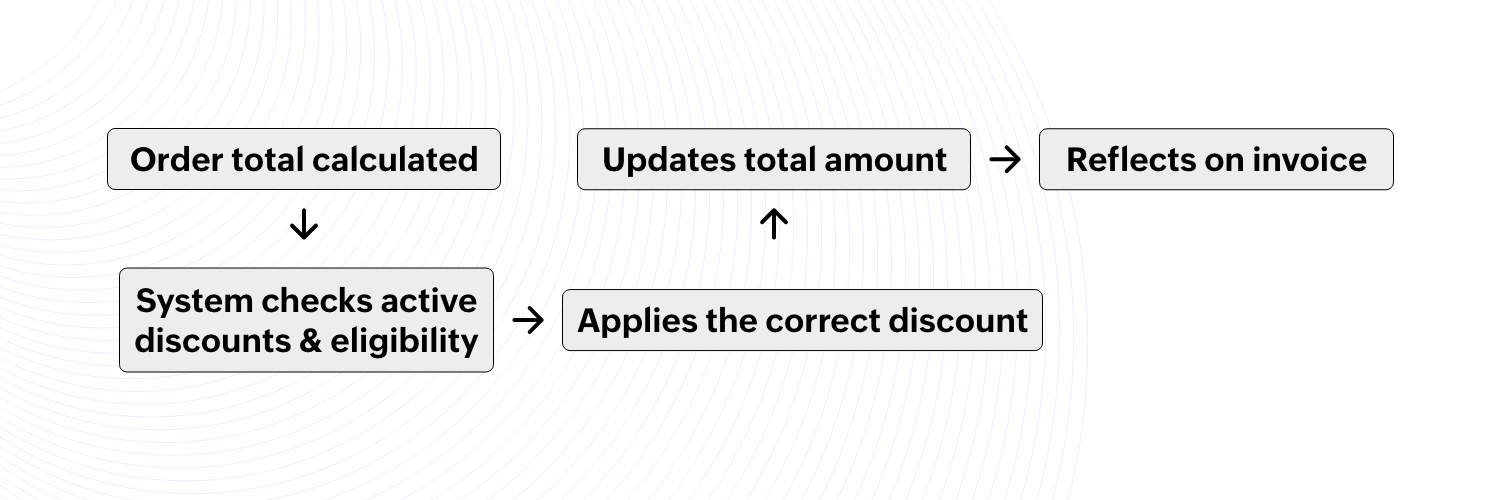
Auto-apply discounts
A customer places an order worth $180, and the system automatically applies a 10% discount based on predefined conditions.
How the automation works:
The system checks the order value against ongoing discounts.
If the total exceeds $150, the discount of 10% is applied (a predefined rule is set here).
The system verifies customer eligibility, such as:
A first-time buyer discount
A loyalty program reward for returning customers
A seasonal promotion that applies to all orders
The discount is automatically added at checkout, and the final price is adjusted.
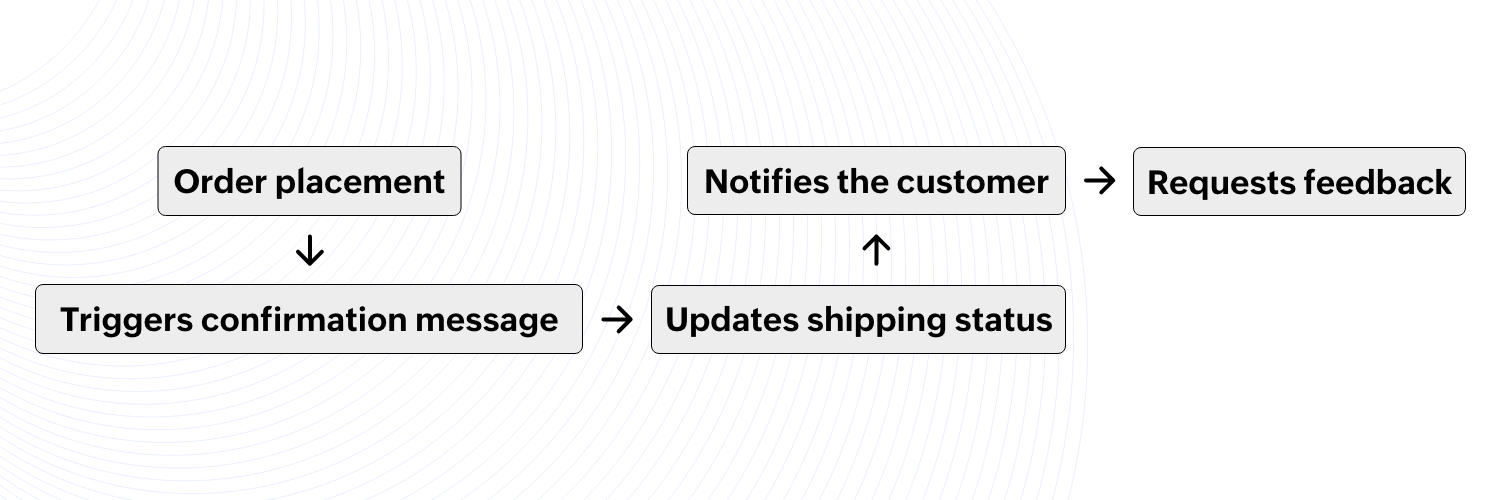
Order success messages
A customer purchases three kitchen appliances, and they expect timely updates. The system ensures smooth communication by sending:
Order confirmation: As soon as payment is received, an automatic email and SMS are triggered, for example:
“Your order (#8453) is confirmed! Estimated delivery: April 25.”
Shipping updates: When the package is handed over to the courier, the system:
Assigns a tracking number.
Sends an update: “Your order has been shipped! Track it here: [Link].”
Delivery confirmation & review request: Once the order status updates to "Delivered," an automated message is sent:
"Your package has arrived. We’d love to hear your feedback!”
Order follow-up reminders
A customer visits an online store, adds two premium watches to the cart, but doesn’t complete the purchase. Instead of losing a potential sale, the system follows up.
How the automation works:
Abandoned cart reminder: After 24 hours, the system is set to send a reminder:
“Still thinking about it? Complete your order before stock runs out!”
Discount incentive (optional): If the customer still doesn’t check out after 48 hours, the system may trigger a limited-time 5% discount.
Post-delivery review request: If the order is completed and delivered, a feedback request is scheduled:
“How was your experience? Rate us and earn reward points!”

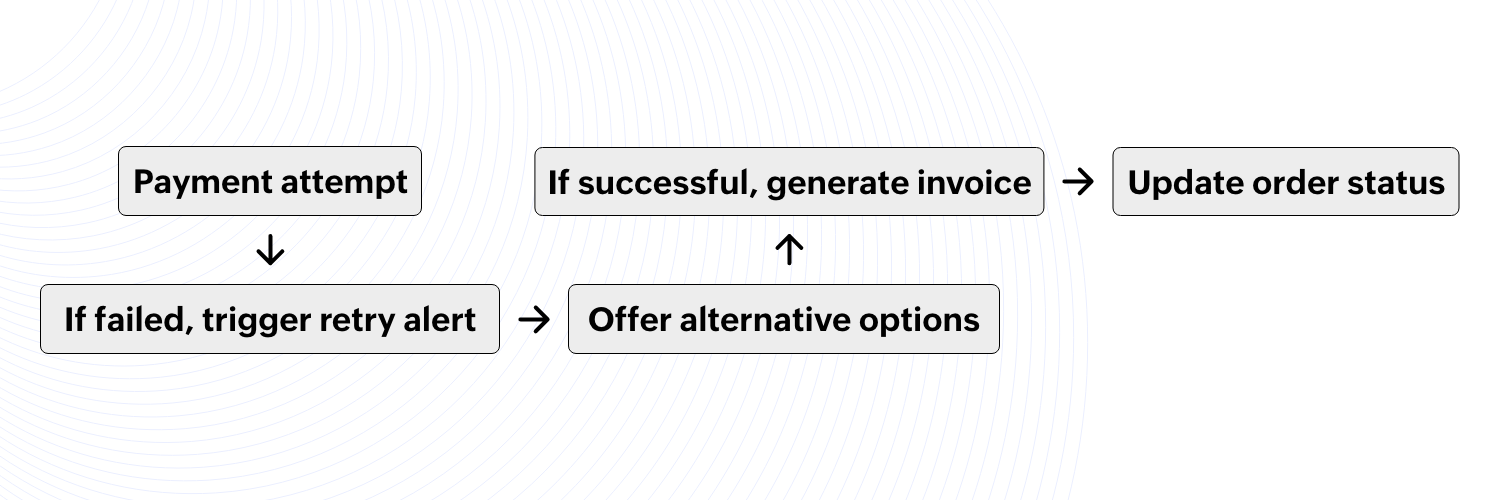
Payment gateway integration and failure handling
A B2B company receives a bulk order for 300 office chairs worth $15,000. However, the buyer's initial payment fails.
The system verifies the payment and detects a failure.
It instantly sends an alert:
“Your payment attempt was unsuccessful. Please try again or use an alternate method.”
If the second attempt fails, the system suggests:
Switching to a bank transfer or financing option.
Offering an installment plan like 50% upfront and 50% after delivery.
Once payment succeeds, an invoice is auto-generated and sent to the buyer’s email.
Final thoughts on transforming how you manage orders
Automating your order management system isn’t just about saving time—it improves accuracy, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. From order capture to post-order analytics, automation helps reduce errors, streamline operations, and enhance CX.
Start with key steps, refine your automation workflows, and scale as needed. The sooner you implement automation, the faster your business will benefit from improved efficiency and a better customer experience!
 Bharathi Monika Venkatesan
Bharathi Monika VenkatesanBharathi Monika Venkatesan is a content writer at Zoho Creator. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring history, reading short novels, and cherishing moments of personal introspection.