- HOME
- Know Your Tech
- Workflow engines & business rule engines: The hidden powerhouses of business automation
Workflow engines & business rule engines: The hidden powerhouses of business automation
- Last Updated : April 30, 2025
- 22 Views
- 6 Min Read
You're automating, but are you automating smart? Most businesses throw technology at their processes without realizing they're missing two critical components: workflow engines and business rule engines. This distinction matters more than most organizations realize. Mistake their roles, and you're setting yourself up for a tangled mess of inefficiencies. Let's take a look at these automation titans and unlock the true potential of your business.
Workflow engines: The path orchestrator
A workflow engine is essentially a sophisticated digital conductor, orchestrating tasks, people, and systems through predefined sequences. It maps out the "what happens next" steps in your business processes, ensuring that work follows the correct path from start to finish.
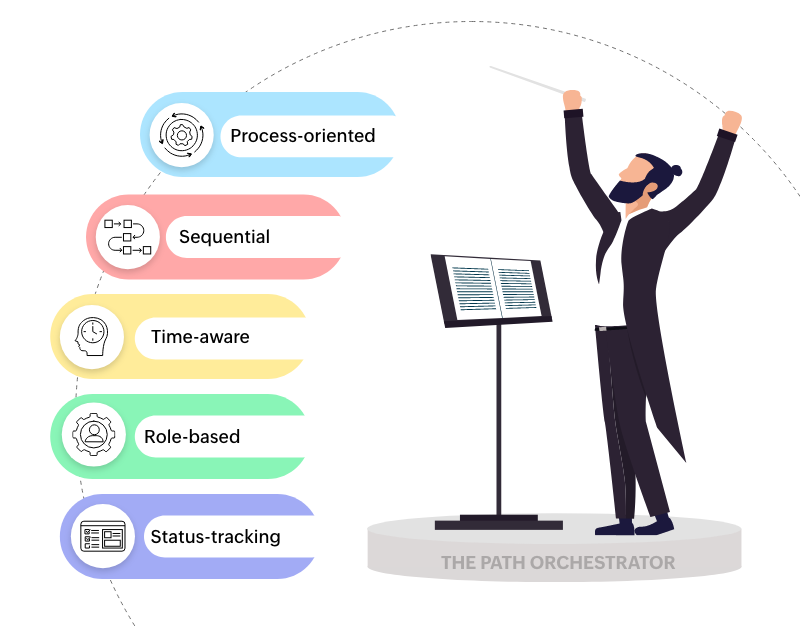
Key characteristics
Process-oriented - Focuses on the journey from point A to point B
Sequential - Manages tasks in order with clear transitions
Time-aware - Tracks durations and deadlines
Role-based - Assigns activities to specific people or departments
Status-tracking - Maintains visibility of where work stands in the process
Workflow engines excel at handling structured processes that follow predictable patterns. They're particularly valuable when coordination between multiple stakeholders is required.
Business rule engines: The decision maker
A business rule engine, by contrast, acts as an automated decision-making system. It evaluates conditions against established rules and determines appropriate actions based on those evaluations—all without human intervention.
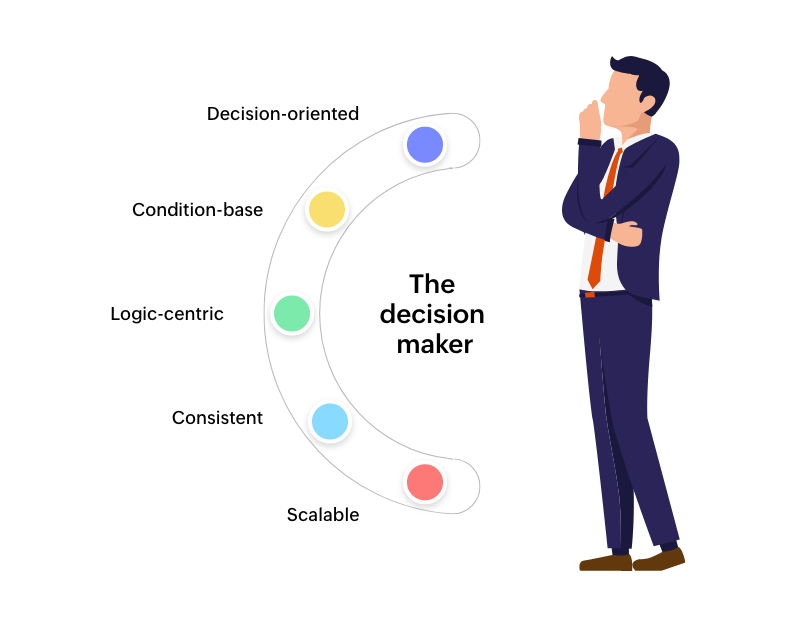
Key characteristics
Decision-oriented - Focuses on determining the correct action
Condition-based - Evaluates "if-then" scenarios
Logic-centric - Applies complex reasoning to business data
Consistent - Ensures uniform application of policies
Scalable - Can apply thousands of rules simultaneously
Business rule engines shine when complex decision-making needs to happen consistently and at scale, especially when business policies change frequently.
The architectural distinction
The fundamental difference lies in their purpose:
Workflow engines orchestrate the movement of work
Business rule engines make decisions about that work
Use a workflow engine when
Process transparency is critical - When stakeholders need visibility into where things stand
Handoffs are frequent - When work regularly moves between different people or departments
Sequential steps matter - When order of operations is crucial
Human approvals are needed - When the process requires human judgment at specific points
Documentation is required - When you need a clear audit trail of process execution
Real-world example: A loan application process that moves from initial submission through verification, underwriting, approval, and funding stages involves multiple departments working in sequence
Use a business rule engine when
Complex decisions are frequent - When numerous factors affect each decision
Rules change often - When business policies evolve regularly
Consistency is paramount - When decisions must be uniform regardless of who makes them
Speed matters - When decisions need to happen instantaneously
Compliance is critical - When adherence to regulations must be automatic
Real-world example: An insurance company determining policy eligibility based on hundreds of risk factors, rating rules, and regulatory requirements
Organizational challenges these engines can fix
Many organizations struggle with operational inefficiencies that silently drain resources and hamper growth. Both workflow and business rule engines target specific pain points that traditional automation often fails to address.
Key organizational challenges
Decision inconsistency - Different employees making vastly different decisions when faced with identical situations, creating customer experience chaos and compliance risks
Process invisibility - Work disappearing into "black holes" with no way to track status or identify bottlenecks
Knowledge dependency - Critical processes relying entirely on the expertise of specific employees, creating dangerous single points of failure
Change resistance - Processes hard coded into systems, requiring expensive developer time for even minor policy adjustments
Scale limitations - Manual decision-making creating throughput ceilings that prevent business growth
For organizations facing these challenges, workflow and business rule engines aren't just nice-to-have technologies—they're essential tools for breaking through operational barriers that conventional approaches can't overcome.
The integration sweet spot
The most sophisticated automation solutions actually combine both engines:
Workflow engines manage the overall process flow.
Business rule engineshandle decision points within those flows.
This powerful combination allows organizations to create intelligent processes that not only follow the right path but make smart decisions along the way.

Workflow engine advantages you might miss
Bottleneck identification - By tracking process metrics, workflow engines reveal where work consistently slows down.
Institutional knowledge preservation - Processes become documented assets rather than tribal knowledge.
Exception handling - Modern workflow engines include sophisticated mechanisms for managing unexpected situations.
Version control for processes - Changes can be tracked, compared, and even rolled back if needed.
Business rule engine advantages that get overlooked
Business-IT alignment - Non-technical stakeholders can often update rules without developer involvement.
Simulation capabilities - Many rule engines allow testing rule changes against historical data.
Natural language processing - Advanced engines can translate human-readable policies into executable rules.
Decision explanation - The best engines can explain exactly why a particular decision was made.
Implementation considerations
When adding either technology to your stack, keep these factors in mind:
For workflow engines
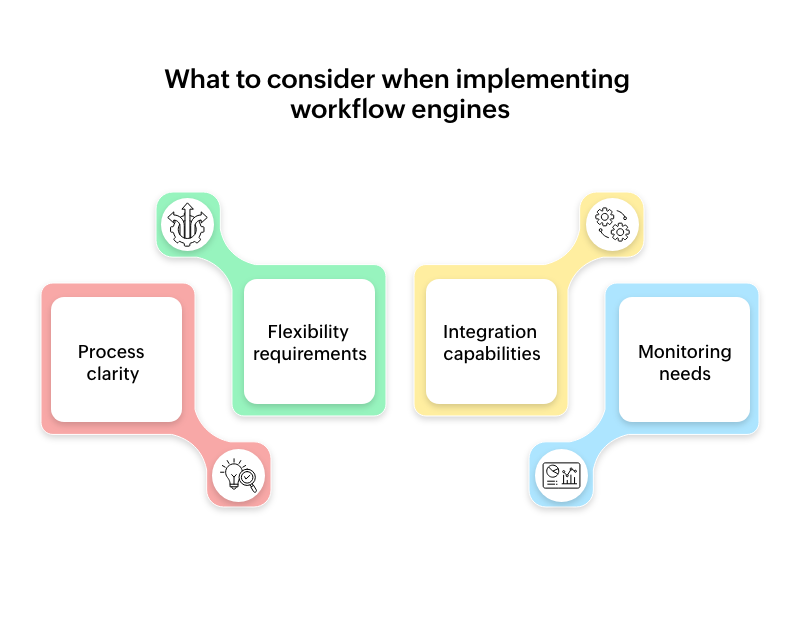
Process clarity - Map your processes thoroughly before implementation.
Flexibility requirements - Some engines favor structure over adaptability.
Integration capabilities - Ensure compatibility with existing systems.
Monitoring needs - Consider what process metrics will be most valuable.
For business rule engines
Rule governance - Establish who can create and modify rules.
Rule complexity - Assess whether simple or complex rule structures are needed.
Performance requirements - Determine how quickly decisions must be rendered.
Testing approach - Plan how rule changes will be verified before deployment.
Example scenario: Imagining workflow and business rule engines in IT service management

Let's take the example of how an imaginary multinational technology corporation could revolutionize its IT service management using the strategic implementation of both workflow and business rule engines.
The challenge
The company was drowning in IT service requests and incident management issues. Support tickets languished in queues, resolution paths varied wildly depending on which technician handled them, and priority decisions were inconsistent. The fragmented approach led to missed SLAs, frustrated employees, and escalating operational costs.
The solution
A sophisticated dual-engine approach that leveraged each technology's strengths:
The business rule engine
Automatically classified incoming tickets based on keywords, system data, and historical patterns
Determined incident severity and priority using complex matrices of impact, urgency, and business criticality
Applied different SLA calculations based on service category, requester department, and business impact
Identified related incidents to detect potential widespread system issues
Recommended knowledge base articles and resolution steps based on incident characteristics
The workflow engine
Routed tickets to appropriate support teams based on classifications determined by the rules engine
Orchestrated multi-step approval processes for change requests and access provisioning
Managed escalation paths when tickets approached SLA thresholds
Coordinated handoffs between Level 1, 2, and 3 support teams
Automated notification workflows to keep stakeholders informed throughout resolution.
The results
The integration of these technologies delivered substantial improvements:
Reduction in mean time to resolution
Increase in first-contact resolution rates
Elimination of orphaned tickets through automated tracking and escalation
Consistent application of IT policies across global support operations
Dramatic improvement in IT customer satisfaction scores
Ability to rapidly implement new IT service policies without recoding applications
This example demonstrates how workflow engines excel at orchestrating the complex movements of IT service tickets through their lifecycle while business rule engines provide the intelligent decision-making needed to classify, prioritize, and direct those tickets. Together, they create a system that's both rigorous and intelligent—exactly what modern IT service management demands.
Future trends to watch
Both technologies are evolving rapidly:
AI integration - Machine learning increasingly complementing traditional rules
No-code interfaces - Making both engines more accessible to business users
Event-driven architectures - Enabling more reactive, less sequential processes
Cloud-native deployments - Offering greater scalability and reduced maintenance
Choose the right engine for your business needs
While workflow engines and business rule engines serve different purposes, they share a common goal: automating aspects of business that previously required manual effort.
The key is understanding which technology addresses your specific challenges. Many organizations find they need both—workflow engines to coordinate activities and business rule engines to embed decision intelligence within those workflows.
By properly distinguishing between these powerful automation tools, you can direct your investment toward the technology that will deliver the greatest business impact for your unique requirements.
Remember: Workflow engines guide the journey and business rule engines make the decisions along the way. Both are essential components in the modern automation toolkit.
 Szhruthi Boopathy
Szhruthi BoopathyPassionate product marketer specializing in low-code and AI-powered app development. When I'm not crafting compelling content and video collaterals, you'll find me immersed in the world of painting or lost in a good book.